Our Sugars
Dr Coy has spent three decades researching natural sugars that provide sustained energy without damaging the body.
These sugars are metabolised differently, avoiding the inflammatory blood-sugar ‘rollercoaster’ that causes anxiety, fatigue, and hunger. These natural sugars are found in small quantities in fruits, vegetables, grains, and milk.
Tagatose
Galactose
Ribose
Isomaltulose
Trehalose
Mannose
Allulose




Claim Approved by the European Food Safety Authority
“Consumption of foods/drinks containing D-tagatose or isomaltulose instead of other sugars induces a lower blood glucose rise after their consumption and contributes to the maintenance of tooth mineralisation compared to sugar-containing foods/drinks.”
Benefits
Low Glycaemic
Prevents High
Blood Sugar
Lower Calorie Content Compared to Household Sugar
Provide Sustained
Energy
Tooth Friendly
The Therapeutic Principle
By understanding how cancer cells use sugar, Dr. Coy realised that specific natural sugars, for example, galactose and mannose, promote a switch in energy metabolisms from the fermentation pathway to the combustion pathway.
Dr Coy’s concept forces cancer cells to switch the way they release energy.
Instead of fermenting sugar to produce energy, cancer cells must burn sugar and other nutrients for energy.
Cancer cells use TKTL1 (the factory in charge of creating cells) and its sugar metabolism pathway to release energy without negative side effects on the cancer cells, and helps them duplicate and spread.
Our body has multiple pathways for creating energy:
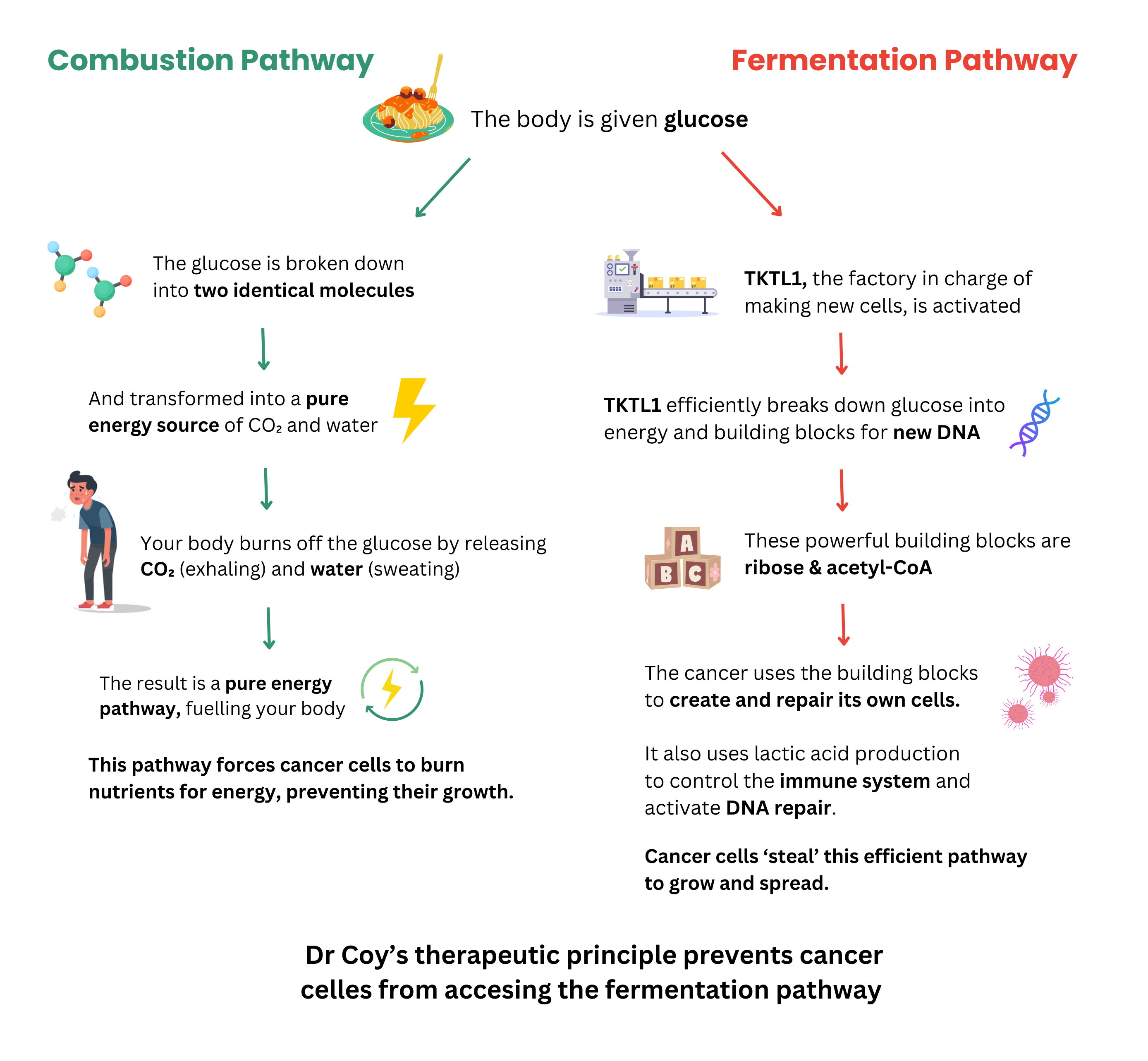
Some of Dr Coy’s sugars, like galactose and mannose inhibit the fermentation pathway but activate the combustion pathway.
Similarly, tagatose cannot be used as a fuel by TKTL1, because it stays in the colon and is used as fuel for good bacteria.
Since TKTL1 cannot use galactose and mannose as fuel, they are not suitable for creating or repairing any new cancer cells.
Therefore, treatments like chemo- and radiotherapy, which are attacking and damaging the DNA of cancer cells, will become much more effective.
Unfortunately, by over activating the TKTL1 metabolism, cancer cells develop the ability to repair the damage caused by chemotherapy and radiotherapy with the formation of the building blocks ribose and acetyl- CoA.
This reduces the effect of chemotherapy and radiotherapy and allows cancer cells to survive.
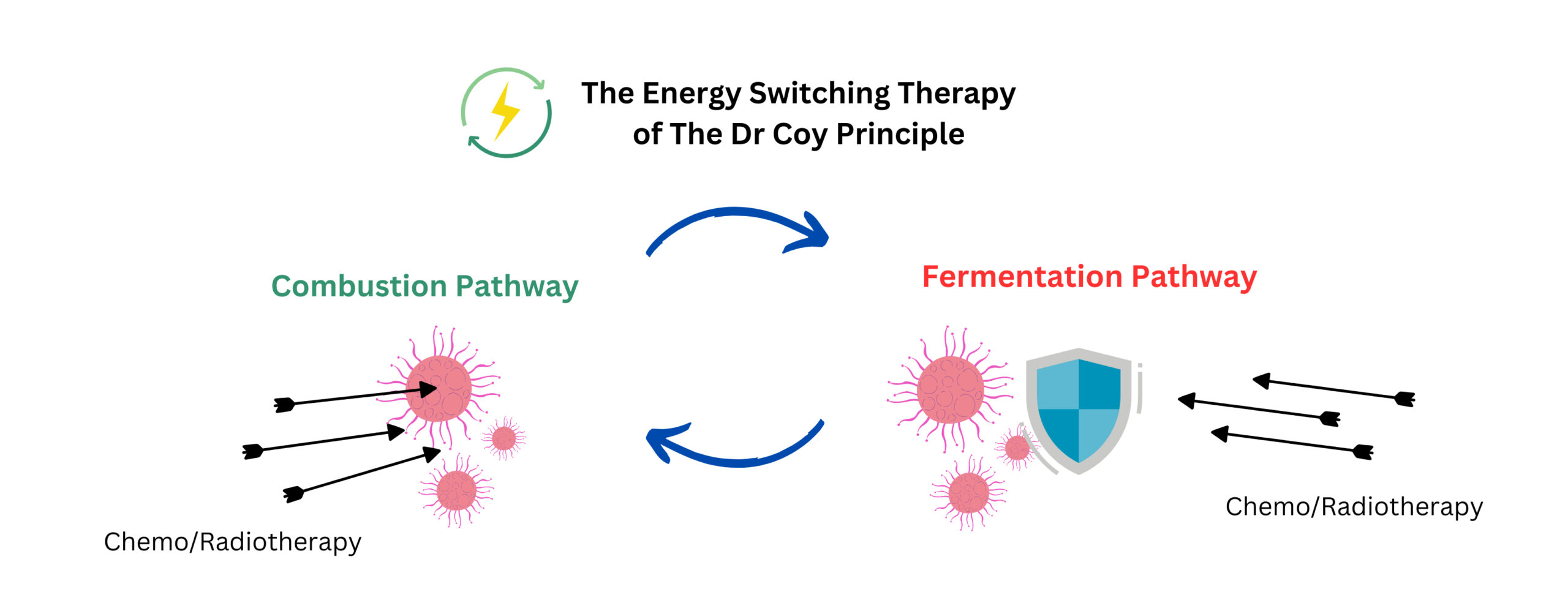
This therapeutic principle was confirmed in the prestigious scientific journal,
Nature Reviews Cancer, April 2010:
The reactivation of the normal metabolism of cancer cells caused chemotherapy and radiotherapy to have an effective impact again
TKTL1 is of fundamental importance
A variety of pharmacological inhibitors are being developed. In particular, the development of a selective therapy, which is non-toxic to healthy cells.
Literature
- Xu X et al 2OO9: IntJ Cancer 2OO9, 124:133O -1337
- Tennant DA et al 2O1O. Nature Reviews Cancer 2O1O, 1O: 267 – 277
- Shibata A et al 2OO8: J Nutr. 2OO8, 138 (11): 2136- 2142
- Sun W et al 2O1O; Clin Cancer Res. 2O1O, 16(3): 857 – 866
- Qutub AA et al 2OO8: Molecular and Cellular Biology 2OO8, 28 (15): 51O6 – 5119
- Otto C et al 2OO8: BMC Cancer 2OO8, 8:122
- Seyfried TI et al 2OO5; Nutrition & Metabolism 2OO5, 2:3°
- Dihal AA et al 2OO8, Proteomics 2OO8, 8:45 – 61
- Walenta S et al 2OOO; Cancer Res 2OOO, 6O: 916 – 921
- Knichwitz G 2OO5: Intensivmedizin up2date 2OO5, 1: 2O5 – 22
- Chen Y, Wu J, Zhai L, Zhang T, Yin H, Gao H, Zhao F, Wang Z, Yang X, Jin M, Huang B, Ding X, Li R, Yang J, He Y, Wang Q, Wang W, Kloeber JA, Li Y, Hao B, Zhang Y, Wang J, Tan M, Li K, Wang P, Lou Z, Yuan J. Metabolic regulation of homologous recombination repair by MRE11 lactylation. Cell. 2O24 Jan 18;187(2):294-311.e21.
- Khodabakhshi A, Akbari ME, Mirzaei HR, Mehrad-Majd H, Kalamian M, Davoodi SH. Feasibility, Safety, and Beneficial Effects of MCT-Based Ketogenic Diet for Breast Cancer Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Trial Study. Nutr Cancer. 2O2O;72(4):627-634.
- Schroeder U, Himpe B, Pries R, Vonthein R, Nitsch S, Wollenberg B. Decline of lactate in tumor tissue after ketogenic diet: in vivo microdialysis study in patients with head and neck cancer. Nutr Cancer. 2O13
- Knopf P, Stowbur D, Hoffmann SHL, Hermann N, Maurer A, Bucher V, Poxleitner M, Tako B, Sonanini D, Krishnamachary B, Sinharay S, Fehrenbacher B, Gonzalez-Menendez I, Reckmann F, Bomze D, Flatz L, Kramer D, Schaller M, Forchhammer S, Bhujwalla ZM, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Schulze-Osthoff K, Pagel MD, Fransen MF, Röcken M, Martins AF, Pichler BJ, Ghoreschi K, Kneilling M. Acidosis-mediated increase in IFN-γ-induced PD-L1 expression on cancer cells as an immune escape mechanism in solid tumors. Mol Cancer. 2O23 Dec 15
